The Windows.edb file is a database file created by Windows Search. It indexes all the files and folders on your system to allow quick and efficient file searches.
However, in some cases, this file can grow incredibly large, causing some concerns about hard drive space. In this article, we will discuss the location, deletion process, and why the Windows.edb file keeps growing in Windows 7, and how to manage it efficiently.
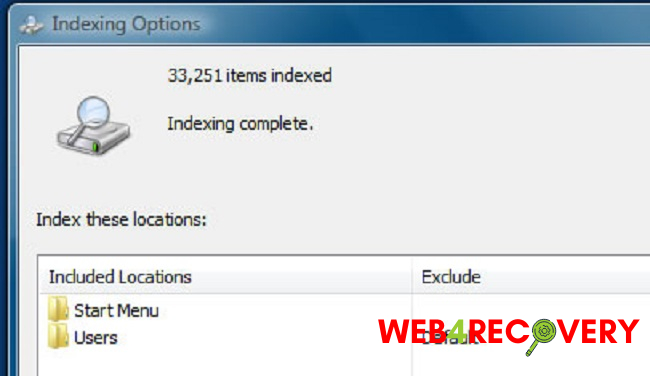
Windows.edb File Location
The Windows.edb file is usually located in the ProgramData\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows directory on the system drive. To access it, you must have Show Hidden Files and Folders enabled, as ProgramData is a hidden folder.
Deleting the Windows.edb File
Before you proceed with deleting the Windows.edb file, it’s crucial to understand that this is a system file. Removing it will affect Windows Search functionality. However, if the file size has become too large, you can reduce it using the following method:
- Go to
Control Panel>Indexing Options. - Click
Modifyand uncheck all the boxes to stop indexing the respective folders. - Click
Advanced>Rebuild.
The Rebuild option will delete and recreate the Windows.edb file. After this process, you can go back to the Indexing Options and recheck the boxes to index the required folders.
Why the Windows.edb File Keeps Growing
The Windows.edb file grows over time because it keeps an index of all files and their changes on your PC.
As you add, remove, or modify files, Windows Search updates the Windows.edb file, leading to growth. In some cases, there may be a glitch causing the file to bloat to an unusually large size.
Path Use and Management of Windows.edb File
Managing the Windows.edb file efficiently is essential for maintaining hard drive space and ensuring smooth system operation. Here’s how you can do this:
- Limit the folders for indexing: By default, Windows Search indexes all locations. Limiting this to crucial folders reduces the
Windows.edbfile size. Navigate toControl Panel>Indexing Options>Modifyand select only the necessary folders for indexing. - Compact the Windows.edb file: Compacting the
Windows.edbfile reduces its size without affecting its functionality. This can be done by navigating toControl Panel>Indexing Options>Advanced>Index Settings>Compact Now. - Move the
Windows.edbfile: If your system drive is running out of space, you can move theWindows.edbfile to a different drive. To do this, go toControl Panel>Indexing Options>Advanced>Index Location>Select new, and choose a new location for yourWindows.edbfile.
Conclusion
The Windows.edb file is integral to the Windows Search functionality, helping speed up file searches. However, its growth needs to be monitored and managed to ensure it doesn’t consume a significant portion of your hard drive space.
With the tips outlined in this guide, you should be able to manage your Windows.edb file effectively in Windows 7. Always remember to proceed with caution when dealing with system files, ensuring not to compromise system integrity and performance.