Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simplified version of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). It’s commonly used for transferring small amounts of data between hosts, such as configuration files or updates.
This detailed guide will dive into enabling TFTP on Windows 10, Windows 7, Linux, Mac, Ubuntu, Debian, and discuss how to use it with tools such as Filezilla, Python, and SolarWinds.
Finally, we’ll tackle a common issue that many users face: “TFTP does not accept options”.
Enabling TFTP on Windows 10 & Windows 7
To facilitate TFTP on Windows, you must install the TFTP client. Let’s walk through the steps for both Windows 10 and Windows 7.
Windows 10:
- Open ‘Control Panel’.
- Select ‘Programs’.
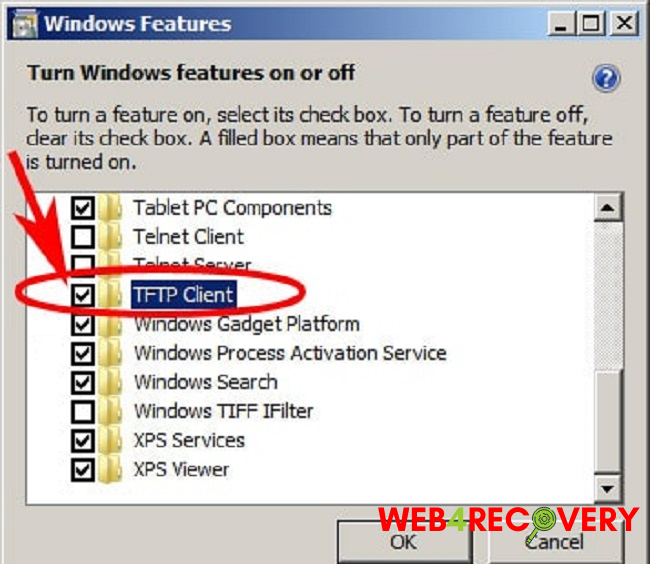
- Choose ‘Turn Windows features on or off’.
- Scroll down to find ‘TFTP Client’.
- Check the box next to ‘TFTP Client’ and click ‘OK’.
Windows 7:
- Click ‘Start’ > ‘Control Panel’.
- Select ‘Programs and Features’.
- In the left pane, click ‘Turn Windows features on or off’.
- Locate ‘TFTP Client’, check its box, and click ‘OK’.
Downloading and Enabling TFTP in Linux, Mac, Ubuntu, and Debian
TFTP is typically pre-installed on Linux and Unix-like operating systems such as Mac, Ubuntu, and Debian. However, in some cases, you might need to download and install the TFTP server package.
Linux:
- Open Terminal.
- Input ‘sudo apt-get install tftp tftpd xinetd’.
- Configure the server as per your requirements.
Mac:
- Open Terminal.
- Type ‘sudo launchctl load -F /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/tftp.plist’.
- To start the TFTP server, type ‘sudo launchctl start com.apple.tftpd’.
Ubuntu & Debian:
- Open Terminal.
- Input ‘sudo apt-get install tftpd’.
- Configure the server according to your needs.
Utilizing TFTP with FileZilla, Python, and SolarWinds
Several software packages and programming languages facilitate TFTP functionality, including FileZilla, Python, and SolarWinds.
FileZilla:
While FileZilla does not natively support TFTP, it does support FTP and SFTP. To incorporate TFTP functionality, you’ll need a different client or third-party plugin.
Python:
Python can gain TFTP functionality using packages like ‘tftpy’. You can install it using pip with the command ‘pip install tftpy’.
SolarWinds:
SolarWinds provides a free TFTP server which you can download from their official website. Once downloaded, run the executable file to install the TFTP server.
Troubleshooting: TFTP Does Not Accept Options
A common issue when using TFTP is encountering a ‘does not accept options’ error. This often results from a mismatch between TFTP clients and servers over optional settings. To resolve this:
- Ensure both the TFTP client and server support the same options.
- Verify that the blocksize value is acceptable to both the client and the server.
TFTP is an essential tool for network and system administrators. Understanding how to enable TFTP across different platforms and integrate it with various applications will enable efficient file transfer operations.
Whether you’re working with Windows, Linux, Mac, Ubuntu, Debian, FileZilla, Python, or SolarWinds, the power of TFTP can streamline your work and boost your productivity.