System File Checker (SFC) is a valuable utility in Windows that scans for and restores missing or corrupted system files.
In this article, we will delve into the details of running SFC, analyzing its logs in Windows 7 and Vista, resolving issues when it’s not working, utilizing it for repair, and using it with external drives.
We’ll also provide specific commands for Windows 10 and 11, examine the DISM tool, explore the concept of Windows Resource Protection, and explain what SFC /scannow does and how it compares to CHKDSK.
Running System File Checker and Analyzing Logs
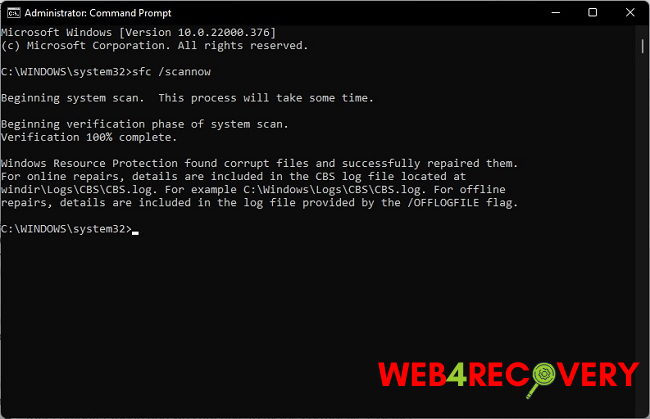
To run the SFC, you need to open Command Prompt as an administrator. The general command to initiate SFC is “sfc /scannow”.
After running this command, SFC will scan all protected system files and replace corrupted files with a cached copy located in a compressed folder at %WinDir%\System32\dllcache.
In Windows 7 and Vista, SFC logs are stored in the CBS.log file, which can be found in the Windows Logs in the System directory.
To access and analyze these logs, open the ‘CBS.log’ file from the path: C:\Windows\Logs\CBS\CBS.log. It’s advisable to make a copy of this log file to analyze it thoroughly.
Troubleshooting SFC When It’s Not Working
If the SFC is not working, it might be due to corrupted system files that the tool can’t fix by itself. In such cases, you can use the Deployment Imaging and Servicing Management (DISM) tool before running the SFC.
DISM can be used to fix the system image, allowing SFC to do its job. The command for this is “DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth”.
Using SFC for Repair and with External Drives
SFC is a handy tool for repairing system files. If a crucial Windows file gets corrupted, SFC can locate the problem and replace the file with a cached copy.
However, SFC doesn’t work directly with external drives. It’s designed to check and repair system files on the computer’s primary operating system drive.
SFC Commands for Windows 10 and 11
The primary SFC command “sfc /scannow” works similarly across Windows 7, 8, 10, and the latest Windows 11. However, there are a few additional commands that can be helpful:
- “sfc /verifyonly”: This command checks the integrity of all system files but doesn’t repair them.
- “sfc /scanfile”: This command allows you to scan a specific file.
Understanding DISM and Windows Resource Protection
DISM is a tool that can be used when the SFC is unable to repair files. It works by fetching fresh copies of corrupted files from the Windows update servers.
Windows Resource Protection (WRP) is a feature that prevents the modification of system files by any means other than specific system procedures. This feature helps SFC maintain the integrity of the system.
What does SFC /Scannow Do?
The “sfc /scannow” command is used to scan all protected system files. If it finds a problem with any of these files, it replaces them with a cached copy located in a compressed folder at %WinDir%\System32\dllcache.
SFC /Scannow vs. CHKDSK
While both SFC /scannow and CHKDSK are system tools used to repair issues, they function differently. SFC focuses on Windows system files, ensuring they are correct and not corrupted.
On the other hand, CHKDSK, short for ‘Check Disk’, is a tool that checks the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors, fixing them where possible. It can also check the disk surface for bad sectors and attempt to recover readable information.
Conclusion
System File Checker is an invaluable tool in Windows, from Vista and Windows 7 up to Windows 10 and 11. It allows users to scan for, and restore, corrupted or missing system files, contributing significantly to the health and stability of your system.
Whether you’re dealing with system crashes, application errors, or unexpected behaviors in Windows, running SFC is a crucial first step in troubleshooting.
While it may not resolve every issue, it is a reliable and important part of maintaining a healthy Windows environment. Understanding its operations and how to use and analyze SFC can go a long way in keeping your system running smoothly.